Summary:
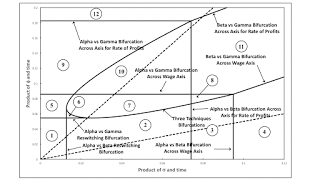
A Bifurcation Diagram with Two Temporal Paths I have a working paper with the post title. Here's the abstract: This article illustrates the application of bifurcation analysis to structural economic dynamics with a choice of technique. A numerical example of the Samuelson-Garegnani model is presented in which technical change is introduced. Examples of temporal paths through the parameter space illustrate variations of the wage frontier. A single technique is initially uniquely cost-minimizing for all feasible rates of profits. Eventually, the technique for which coefficients of production decrease at the fastest rates is always cost-minimizing. During the transition between these positions, reswitching, the recurrence of techniques, and capital-reversing can arise. This example
Topics:
Robert Vienneau considers the following as important: Example in Mathematical Economics, Sraffa Effects, Towards Complex Dynamics
This could be interesting, too:
A Bifurcation Diagram with Two Temporal Paths I have a working paper with the post title. Here's the abstract: This article illustrates the application of bifurcation analysis to structural economic dynamics with a choice of technique. A numerical example of the Samuelson-Garegnani model is presented in which technical change is introduced. Examples of temporal paths through the parameter space illustrate variations of the wage frontier. A single technique is initially uniquely cost-minimizing for all feasible rates of profits. Eventually, the technique for which coefficients of production decrease at the fastest rates is always cost-minimizing. During the transition between these positions, reswitching, the recurrence of techniques, and capital-reversing can arise. This example
Topics:
Robert Vienneau considers the following as important: Example in Mathematical Economics, Sraffa Effects, Towards Complex Dynamics
This could be interesting, too:
Robert Vienneau writes Austrian Capital Theory And Triple-Switching In The Corn-Tractor Model
Robert Vienneau writes Double Fluke Cases For Triple-Switching In The Corn-Tractor Model
Robert Vienneau writes The Emergence of Triple Switching and the Rarity of Reswitching Explained
Robert Vienneau writes Recap For A Triple -Switching Example
|
| A Bifurcation Diagram with Two Temporal Paths |
This article illustrates the application of bifurcation analysis to structural economic dynamics with a choice of technique. A numerical example of the Samuelson-Garegnani model is presented in which technical change is introduced. Examples of temporal paths through the parameter space illustrate variations of the wage frontier. A single technique is initially uniquely cost-minimizing for all feasible rates of profits. Eventually, the technique for which coefficients of production decrease at the fastest rates is always cost-minimizing. During the transition between these positions, reswitching, the recurrence of techniques, and capital-reversing can arise. This example emphasizes the importance of fluke switch points and illustrates possible variations in the existence of Sraffa effects.
 Heterodox
Heterodox
