Steve Hutkins at Save The Post Office continues with the documentation of issues and occurrences at the USPO. Steve presents a good take-down of what DeJoy’s plan is going forward. He is predicting a 3.6% increase on top of a CPI increase. There are two alternatives being presented, the Base case and the “Delivering for America” Case. The “Delivering for America” Case uses the new rate authority to make its calculations (Figure 35, p. 51). It projects that revenues in 2030 will fall to .2 billion (as opposed to .2 billion in the Base Case). I am duplicating what is in Steve’s Report. Best if you read it for yourself. What the USPS 10-year plan may have to say about future rate increases, Steve Hutkins, Save The Post Office The mailers
Topics:
run75441 considers the following as important: politics, Save The Post Office, Steve Hutkins, Taxes/regulation, USPS
This could be interesting, too:
Robert Skidelsky writes Lord Skidelsky to ask His Majesty’s Government what is their policy with regard to the Ukraine war following the new policy of the government of the United States of America.
Joel Eissenberg writes No Invading Allies Act
Ken Melvin writes A Developed Taste
Bill Haskell writes The North American Automobile Industry Waits for Trump and the Gov. to Act
Steve Hutkins at Save The Post Office continues with the documentation of issues and occurrences at the USPO. Steve presents a good take-down of what DeJoy’s plan is going forward. He is predicting a 3.6% increase on top of a CPI increase.
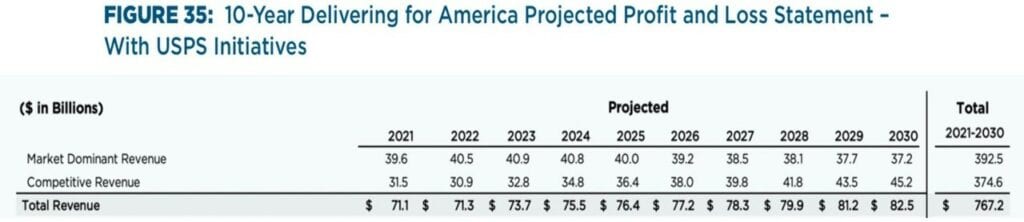
There are two alternatives being presented, the Base case and the “Delivering for America” Case. The “Delivering for America” Case uses the new rate authority to make its calculations (Figure 35, p. 51). It projects that revenues in 2030 will fall to $37.2 billion (as opposed to $32.2 billion in the Base Case). I am duplicating what is in Steve’s Report. Best if you read it for yourself.

What the USPS 10-year plan may have to say about future rate increases, Steve Hutkins, Save The Post Office
The mailers were probably disappointed that the Postal Service’s new 10-year plan released yesterday, “Delivering for America,” did not reveal how big of a rate increase the Postal Service intends to make using the new authority it was granted by the Postal Regulatory Commission. While they wait in suspense, here’s a guess: 3.6 percent.
We already know that the calculations the Postal Service submitted to the PRC in February indicate the hike could be as large as 5.56 percent (on top of the CPI increase), but the new system allows some of the rate authority to be banked for future years, so the increase could be smaller. And that is just what the following analysis suggests.
This analysis is based on two tables and a couple of comments that appear in the 10-year plan. The tables show revenue and expenses under two scenarios, a base case using the status quo and an alternative that uses the revenue and cost savings under the Delivering for America plan. The tables contain numbers for projected volumes and revenues over the next ten years that can be used to estimate what the Postal Service is planning for future price increases under the new rate authority.
The Base Case assumes total mail and package volumes will fall to 82.6 billion by 2030 (Figure 28, p. 46), with 6.6 billion pieces of that in packages (p. 42). Market Dominant volumes in FY 2030 are thus projected to be around 76 billion pieces. The Base Case table also provides Market Dominant revenues for each year, with revenues in 2030 falling to $32.2 billion.
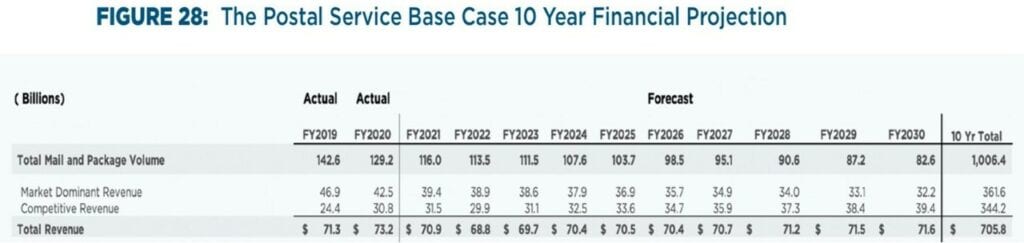
The Base Case assumes rate increases at the current CPI cap, which has been about 2 percent over the past few years. Using these assumptions, one can calculate what the Postal Service is projecting for annual volumes for Market Dominant products.
The “Delivering for America” Case uses the new rate authority to make its calculations (Figure 35, p. 51). It projects that revenues in 2030 will fall to $37.2 billion (as opposed to $32.2 billion in the Base Case).
If one assumes volumes over the next ten years turn out to be the same as in the base case (which is optimistic, since a rate increase may negatively impact volumes), one can calculate the average revenue per piece and the annual rate increases under both scenarios.
Here’s a table pulling these projections and estimates together. It uses the annual revenues as shown for both scenarios in the 10-year plan’s tables, the volume for FY20 as stated in the Revenue, Piece and Weight Report and for FY2030 as indicated by the 10-year plan, and a CPI of 2 percent. The other calculations are derived from these numbers.
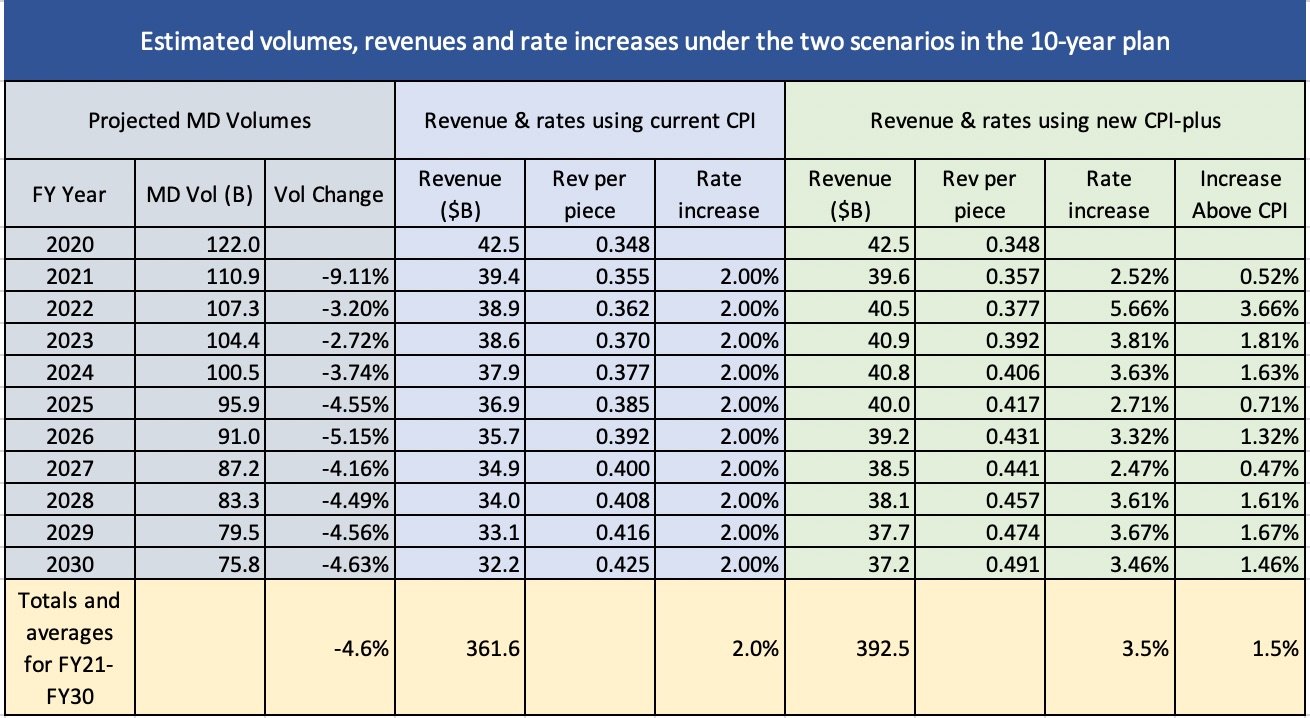
The Postal Service appears to expect annual volume declines of about 4.5 percent for Market Dominant products — significantly more than the 3 percent declines of the past decade, but within reason.
The bottom line shows that under the Base Case over the next ten years revenues will total about 361.6 billion compared to 392.5 billion under the “Delivering for America” Case — a difference of about $31 billion.
A table in the 10-year plan (Figure 29, p. 47) says the revenue impact of implementing the new rate authority will range from $35 billion to $52 billion. It’s not clear how the Postal Service came up with this larger estimate, but it suggests that $30 billion is a conservative estimate for what the new rate authority will bring in.

In any case, increasing Market Dominant revenues by $30 billion over ten years at the same time volumes are declining by about 4.6 percent a year would require rate increases averaging around 1.5 percent above a CPI of 2 percent.
As for FY 2021 and FY 2022, the above analysis suggests that whatever the rate increase may turn out to be for this year, it won’t have much effect on FY21 revenues because it won’t be implemented until the fiscal year is almost over. The two tables in the 10-year plan indicate that the Postal Service is projecting about $200 million more in revenues under the new pricing authority.
The analysis suggests, however, that next year the increase could be on the order of 5.6 percent — 2 percent for the CPI, and 3.6 percent under the new rate authority.
This is all just speculation, of course. The Postmaster General should be announcing the new rate increase sometime soon, and the guessing game will be over.
