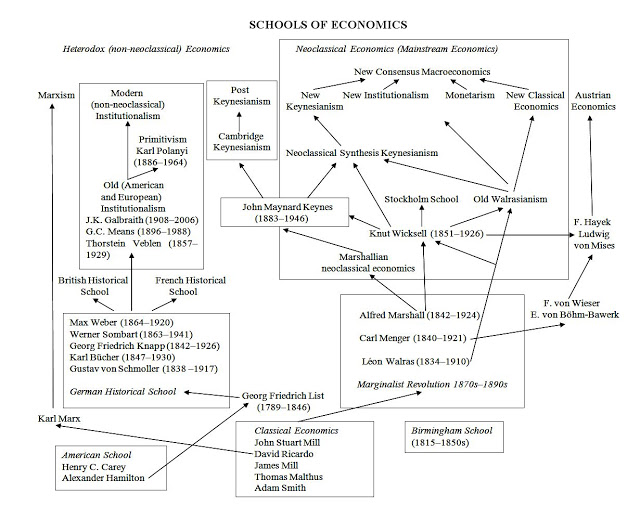
I was pleased to see my older diagram used here in a critique of Noah Smith.Some people pointed out that Knut Wicksell, given his influence, needs to be included in the diagram. That is true.So I have revised the diagram as follows (open in a separate window to see it properly): I have included Knut Wicksell, the American School (Henry C. Carey and Alexander Hamilton), Georg Friedrich List, the Birmingham School, the Stockholm School, and Karl Polanyi and Primitivism.On Knut Wicksell, see here and here.For good discussion of Wicksell’s theories, see Axel Leijonhufvud “The Wicksell Connection: Variations on a Theme” (1981), Colin Rogers’ Money, Interest and Capital: A Study in the Foundations of Monetary Theory (1989), and David Laidler’s Fabricating the Keynesian Revolution (1999).Knut Wicksell’s development of the loanable funds theory with the natural rate of interest has been one of his most influential contributions to economics. For Wicksell a market economy has a long-run tendency to monetary equilibrium, and his monetary equilibrium approach was adopted and developed in diverse ways by many important schools: namely, the (1) the Stockholm School; (2) the Marshallian neoclassical school, (3) the Austrians and (4) the modern New Consensus macroeconomics.BIBLIOGRAPHY Laidler, David E. W. 1999.
Topics:
Lord Keynes considers the following as important: A Revised Diagram of Economics Schools
This could be interesting, too:
Some people pointed out that Knut Wicksell, given his influence, needs to be included in the diagram. That is true.
So I have revised the diagram as follows (open in a separate window to see it properly):
I have included Knut Wicksell, the American School (Henry C. Carey and Alexander Hamilton), Georg Friedrich List, the Birmingham School, the Stockholm School, and Karl Polanyi and Primitivism.
On Knut Wicksell, see here and here.
For good discussion of Wicksell’s theories, see Axel Leijonhufvud “The Wicksell Connection: Variations on a Theme” (1981), Colin Rogers’ Money, Interest and Capital: A Study in the Foundations of Monetary Theory (1989), and David Laidler’s Fabricating the Keynesian Revolution (1999).
Knut Wicksell’s development of the loanable funds theory with the natural rate of interest has been one of his most influential contributions to economics.
For Wicksell a market economy has a long-run tendency to monetary equilibrium, and his monetary equilibrium approach was adopted and developed in diverse ways by many important schools: namely, the (1) the Stockholm School; (2) the Marshallian neoclassical school, (3) the Austrians and (4) the modern New Consensus macroeconomics.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Laidler, David E. W. 1999. Fabricating the Keynesian Revolution: Studies of the Inter-War Literature on Money, the Cycle, and Unemployment. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Leijonhufvud, Axel. 1981. “The Wicksell Connection: Variations on a Theme,” in Axel Leijonhufvud, Information and Coordination: Essays in Macroeconomic Theory. Oxford University Press, Oxford and New York. 131–202.
Rogers, C. 1989. Money, Interest and Capital: A Study in the Foundations of Monetary Theory. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.