A considerable body of literature has been published, during the last century, arguing that a movement away from competitive markets must be recognized in trying to describe and understanding contemporary capitalism. The literature I am thinking of emphasizes big business, corporations, and finance. Here are some selections, not all of which I have read: Rudolf Hilferding (1910). Finance Capital: A study of the latest phase of capitalist development. Adolfe A. Berle and Means (1932). The...
Read More »The Labor Theory of Value and Sraffa’s Standard Commodity with Markup Pricing
I have uploaded a working paper with the post title. Abstract: This article demonstrates relationships that are transparent in Sraffa's standard system hold even when relative rates of profit vary persistently among industries. Even with such variations, total constant capital, total variable capital, total surplus value, and the rate of profits are unaltered by evaluation at labor values and at prices of production in Sraffa’s standard system. These results buttress those who see in the...
Read More »Foreign Trade And Non-Uniform Rates Of Profits
This post raises a question. Supposedly, the classical concept of prices of production with non-uniform rates of profits can be recast as a theory of foreign trade. I do not see how wages can properly be treated in such recasting. D'Agata (2018) and Zambelli (2018) are two recent papers that argue prices of production can be formulated with non-uniform rates of profits. They argue that this introduces a certain indeterminateness into prices, as in some of my examples of foreign trade....
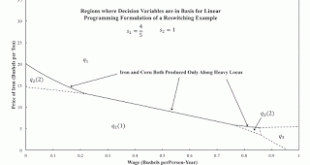
Read More »A Linear Program for Markup Pricing
Figure 1: A Partition of Price-Wage Space for a Two-Commodity Reswitching Example1.0 Introduction This post generalizes my approach in Vienneau (2005). In that article, I present a Linear Programming (LP) problem for the firm. In the case of an economy that produces two commodities, one can present a graphical display that clarifies how Sraffa's equations arise. The dual LP is important in this development. Here, I show how that approach can work for a case in which rates of profits...
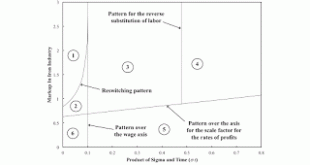
Read More »Extending An Example With Markup Pricing
Figure 1: A Two-Dimensional Pattern Diagram The example in this working paper is of an economy in which two commodities are produced. Technical progress is modeled as decreasing the coefficients of production in one of the processes for producing corn. They decrease at a rate of σ of ten percent. Figure 2 shows how the pattern of switch points vary with technical progress. Initially, the Beta technique is cost-minimizing. Then it becomes a reswitching example. Around the switch point at...
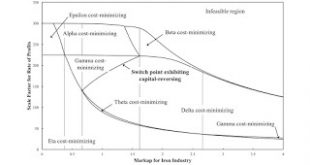
Read More »Workers Benefiting From Increased Markups In Selected Industries
Figure 1: Variation in Switch Points with the Markup in the Iron Industry1.0 Introduction I finally use the tools of pattern analysis that I have been inventing to tell a practical story. I build on the example which I began in my previous post. Workers would be better off if an increase in wages led to greater employment, not less. A long-period change in relative markups among industries can result in firms in some industries obtaining a greater rate of profits at the expense of firms...
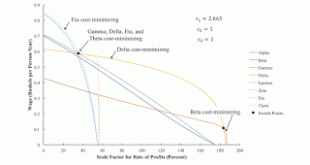
Read More »One Technique Replacing Another: An Example
Figure 1: The Wage Frontier at a Four-Technique Patterns1.0 Introduction This post presents another numerical example of one technique replacing another, along the wage frontier, with a perturbation of a model parameter. In a previous post, I identified three sequences of patterns of switch points in which the wage curves for one technique replaces the wage curve of another. In one of these sequences, a three-technique pattern removes the middle technique from three techniques with wage...
Read More »Bifurcations And Switchpoints
I have organized a series of my posts together into a working paper, titled Bifurcations and Switch Points. Here is the abstract: This article analyzes structural instabilities, in a model of prices of production, associated with variations in coefficients of production, in industrial organization, and in the steady-state rate of growth. Numerical examples are provided, with illustrations, demonstrating that technological improvements or the creation of differential rates of profits can...
Read More »Bifurcation Analysis in a Model of Oligopoly
Figure 1: Bifurcation Diagram I have presented a model of prices of production in which the the rate of profits differs among industries. Such persistent differential rates of profits may be maintained because of perceptions by investors of different levels of risk among industries. Or they may reflect the ability of firms to maintain barriers to entry in different industries. In the latter case, the model is one of oligopoly. This post is based on a specific numeric example for...
Read More » Heterodox
Heterodox