The crisis of the ‘yellow vests’ raises a key issue both in France and in Europe, namely that of fiscal justice. Since his election, Emmanuel Macron has spent considerable time in explaining to the country that the « premiers de cordée », i.e. the leading fortunes and industrialists, should be treated with care; the top priority was to grant tax cuts to the wealthiest, and as a start, the wealth tax abolished. All this was done at top speed, in a spirit of invincibility and without the slightest qualm of conscience. Even Nicolas Sarkozy had been wiser in 2007 with his ‘tax shield’ which he did nevertheless have to cancel in 2012. Inevitably all those who do not consider themselves to be ‘leading lights’ have felt abandoned and humiliated by the Macron discourse, and this is how we
Topics:
Thomas Piketty considers the following as important: in-english, Non classé
This could be interesting, too:
Thomas Piketty writes Regaining confidence in Europe
Thomas Piketty writes Trump, national-capitalism at bay
Thomas Piketty writes Democracy vs oligarchy, the fight of the century
Thomas Piketty writes For a new left-right cleavage
The crisis of the ‘yellow vests’ raises a key issue both in France and in Europe, namely that of fiscal justice. Since his election, Emmanuel Macron has spent considerable time in explaining to the country that the « premiers de cordée », i.e. the leading fortunes and industrialists, should be treated with care; the top priority was to grant tax cuts to the wealthiest, and as a start, the wealth tax abolished. All this was done at top speed, in a spirit of invincibility and without the slightest qualm of conscience. Even Nicolas Sarkozy had been wiser in 2007 with his ‘tax shield’ which he did nevertheless have to cancel in 2012. Inevitably all those who do not consider themselves to be ‘leading lights’ have felt abandoned and humiliated by the Macron discourse, and this is how we now find ourselves in the present situation. The current leadership has committed a series of factual, historical and political errors which it is urgent and possible to correct today.
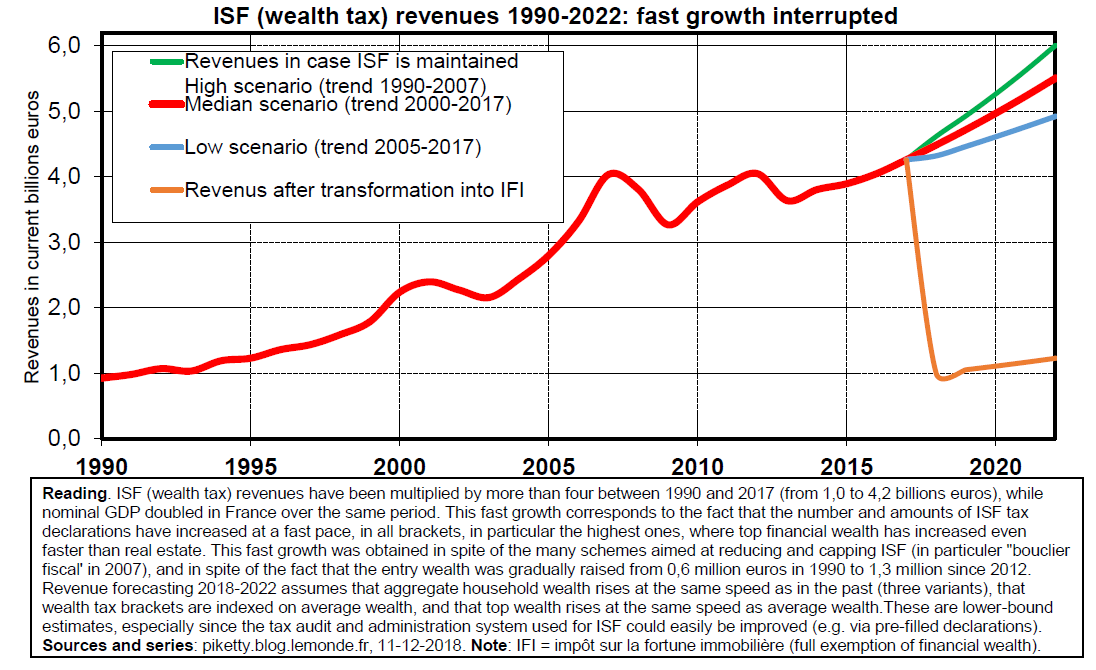
In the first instance, Macron attempted to justify the abolition of the wealth tax by stating that this tax was instrumental in wealth leaving France. The problem is that this statement is totally unfounded from a factual point of view. Since 1990 we have witnessed a spectacular and continuous rise in the number of estates and amounts of wealth declared to the wealth tax. This development has taken place in all bands of the wealth tax, in particular in the highest bands, where the number and amount of financial assets has risen even faster than the holdings in real estate, which in turn have risen more rapidly than the GDP and the total payroll. The falls in the stock exchange in 2001 and 2008 meant a temporary calm in this evolution but, as soon as the crises ended, the long-term trends picked up again.
In total, the income from the wealth tax (ISF) more than quadrupled between 1990 and 2017, rising from 1 billion to over 4 billions, whereas the nominal GDP was only multiplied by two. All this despite the numerous reductions, exemptions and capping granted over the years to the wealth tax payers and despite the fact that the threshold for inclusion in the wealth tax (ISF) has gradually been raised from 0.6 million Euros of net wealth in 1990 to 1.3 million Euros since 2012 (after deduction of 30% on the value of the main residence of the household). Furthermore, the fiscal control of this tax has always been inadequate.
We just have to consider, for example, that the pre-filled returns have been in place for 10 years for income tax, but they have never been applied for the wealth tax, whereas the banks could easily transmit all the information required to the tax authorities. In 2012, the detailed tax declaration above 3 million Euros was even abolished (since then all that is required is a global amount of wealth with no possibility of systematic control). With improved administration, the wealth tax (ISF) could today yield over 10 billion Euros. Moreover this is in no way surprising, bearing in mind the fact that the property tax yields over 40 billion Euros and that the wealth tax is extremely concentrated (especially the financial assets, exempted from property tax).
The fact remains that in the present state of the law and the administration of the wealth tax (ISF), both of which are defective, the revenue from this tax has nevertheless risen from 1 to 4 billion between 1990 and 2017. Given the evolution in wealth, it should have risen to almost 6 billion in 2022. With the abolition of the wealth tax (ISF) and the implementation of the IFI (Ipôt sur le fortune immobilière, i.e. tax on real estate wealth, excluding all financial assets), the revenue has fallen to just over 1 billion in 2018. Between now and 2022 we will have lost 5 billion Euros per year and find ourselves back at the level we were at thirty years ago.
The government’s second mistake is historical: they are in the wrong time-period. It is undeniable that the United States and the United Kingdom launched a process of dismantling fiscal progressivity in the 1980s and that this movement was partly followed in Europe in the 1990s and at the beginning of the years 2000 – for example with the suspension of the wealth tax in Germany and Sweden (and as a bonus that of the inheritance tax in the latter case).
But are we really so sure that these policies produced the effects expected? Since the crisis in 2008, and even more so since Trump, Brexit and the explosion of the xenophobe vote all over Europe, there is a better appreciation of the dangers posed by the rise in inequality and the sense of abandonment in the working classes, so that many now understand the need for a new social regulation of capitalism. In these conditions, adding a further measure in favour of the richest in 2018 was not really very clever. If Macron wants to be the president of the 2020s and not the 1990s, he is going to have to adapt quickly.
The saddest thing is the appalling wastage and mess concerning global warming. If a carbon tax is to succeed, it is imperative that the totality of the net proceeds be allocated to the social measures associated with the ecological transition. The government has done just the opposite: only 10% of the 4 billion Euros rise in fuel duty in 2018, and the extra 4 billion expected in 2019, were earmarked for social measures, while the remainder financed, de facto, the abolition of the wealth tax (ISF) and the flat tax on income from capital.
If Macron wants to save his five-year period in power, he must immediately re-instate the wealth tax and allocate the revenue to compensate those who are the most affected by the rises in carbon tax, which must continue.
If he does not do so, that will mean that he will have opted for an outdated pro-rich ideology at the expense of the campaign against global warming.
PS1: series used for the graph on ISF tax revenues are available here.
PS2: series on the rise of wealth in France are available there, and in a more detailed manner in this article.
