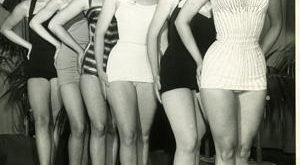[embedded content] Advertisements
Read More »The face of a real hero
The face of a real hero French policeman Arnaud Beltrame, shot to death by an Islamist gunman when he swapped himself for a hostage in a supermarket siege in the southwest town of Trèbes. Advertisements
Read More »Keynes’ beauty contest
Professional investment may be likened to those newspaper competitions in which the competitors have to pick out the six prettiest faces from a hundred photographs, the prize being awarded to the competitor whose choice most nearly corresponds to the average preferences of the competitors as a whole; so that each competitor has to pick not those faces which he himself finds prettiest, but those which he thinks likeliest to catch the fancy of the other competitors, all of whom...
Read More »Assar Lindbeck-medaljen
Sveriges nationalekonomer träffas i höst på Linnéuniversitet i Växjö för en numera återkommande vartannat års-konferens. Utöver forskningsseminarier arrangeras utdelning av Assar Lindbeck-medaljen … [embedded content] Advertisements
Read More »Juloratoriet (personal)
[embedded content] Filmer kan beröra oss på många olika sätt. De flesta är spännande eller roliga tidsfördriv. Men sen finns också de riktigt stora filmerna. De som tar tag i oss och tränger djupt under skinnet och skakar om oss. För alltid. Kjell-Åke Anderssons filmatisering av Göran Tunströms Juloratoriet — med gudabenådad musik av Stefan Nilsson — är en sådan film. Det är en av de sorgligaste filmer som kan ses. Men på samma gång kanske också den allra vackraste. Den om...
Read More »Jerry Williams (1942-2018)
[embedded content] En legend har gått ur tiden. Och ja, det stora vemodet rullar in, när man tänker på alla dessa år denne ‘working class hero’ med allt sitt engagemang, sociala patos och musik spridit glädje och ljus i våra liv. R.I.P. Advertisements
Read More »Why game theory never will be anything but a footnote in the history of social science
Why game theory never will be anything but a footnote in the history of social science Half a century ago there were widespread hopes game theory would provide a unified theory of social science. Today it has become obvious those hopes did not materialize. This ought to come as no surprise. Reductionist and atomistic models of social interaction – such as the ones mainstream economics and game theory are founded on – will never deliver sustainable building...
Read More »Keynes’ critique of econometrics — still valid after all these years
Keynes’ critique of econometrics — still valid after all these years To apply statistical and mathematical methods to the real-world economy, the econometrician has to make some quite strong assumptions. In a review of Tinbergen’s econometric work — published in The Economic Journal in 1939 — John Maynard Keynes gave a comprehensive critique of Tinbergen’s work, focusing on the limiting and unreal character of the assumptions that econometric analyses build...
Read More »McCloskeyian rhetoric
This is not new to most of you of course. You are already steeped in McCloskey’s Rhetoric. Or you ought to be. After all economists are simply telling stories about the economy. Sometimes we are taken in. Sometimes we are not. Unfortunately McCloskey herself gets a little too caught up in her stories. As in her explanation as to how she can be both a feminist and a free market economist: “The market is the great liberator of women; it has not been the state, which is after all...
Read More »Programmet som gör det värt att betala varenda krona i radio- och tv-avgiften
Programmet som gör det värt att betala varenda krona i radio- och tv-avgiften I dessa tider, när ljudrummet dränks i den kommersiella radions tyckmyckentrutade ordbajseri och fullständigt intetsägande pubertalflamsande tjafs, har man nästan gett upp. Men det finns ljus i mörkret. I programmet Text och musik med Eric Schüldt — som sänds på söndagsförmiddagarna i P2 mellan klockan 11 och 12 — kan man lyssna på seriös musik och en programledare som har något...
Read More » Lars P. Syll
Lars P. Syll