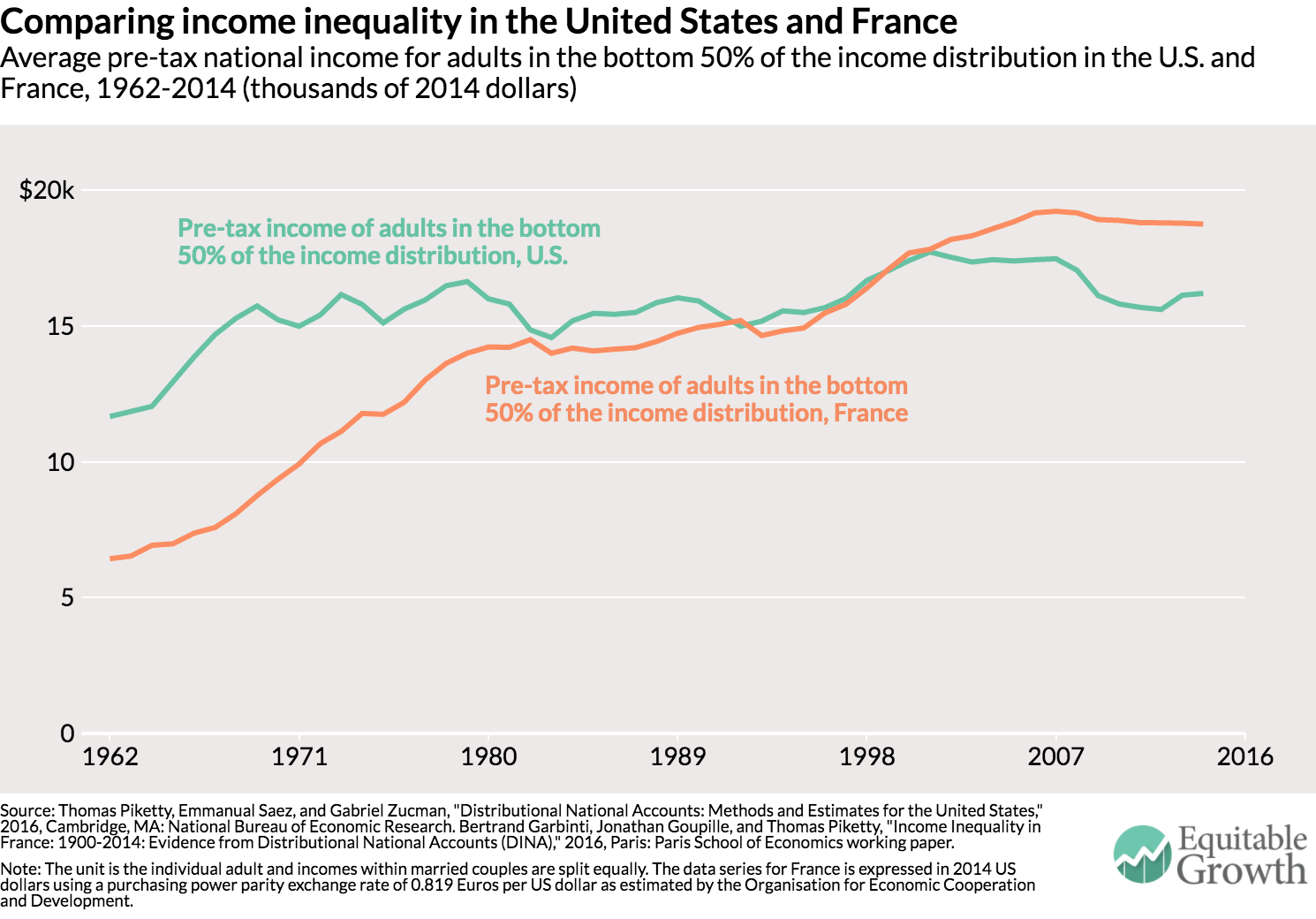
The bottom 50 percent of income earners makes more in France than in the United States even though average income per adult is still 35 percent lower in France than in the United States (partly due to differences in standard working hours in the two countries).9 Since the welfare state is more generous in France, the gap between the bottom 50 percent of income earners in France and the United States would be even greater after taxes and transfers. The diverging trends in the distribution of pre-tax income across France and the United States—two advanced economies subject to the same forces of technological progress and globalization—show that working-class incomes are not bound to stagnate in Western countries. In the United States, the stagnation of bottom 50 percent of incomes
Topics:
Editor considers the following as important: Uncategorized
This could be interesting, too:
tom writes The Ukraine war and Europe’s deepening march of folly
Stavros Mavroudeas writes CfP of Marxist Macroeconomic Modelling workgroup – 18th WAPE Forum, Istanbul August 6-8, 2025
Lars Pålsson Syll writes The pretence-of-knowledge syndrome
Dean Baker writes Crypto and Donald Trump’s strategic baseball card reserve
The bottom 50 percent of income earners makes more in France than in the United States even though average income per adult is still 35 percent lower in France than in the United States (partly due to differences in standard working hours in the two countries).9 Since the welfare state is more generous in France, the gap between the bottom 50 percent of income earners in France and the United States would be even greater after taxes and transfers.
The diverging trends in the distribution of pre-tax income across France and the United States—two advanced economies subject to the same forces of technological progress and globalization—show that working-class incomes are not bound to stagnate in Western countries. In the United States, the stagnation of bottom 50 percent of incomes and the upsurge in the top 1 percent coincided with drastically reduced progressive taxation, widespread deregulation of industries and services, particularly the financial services industry, weakened unions, and an eroding minimum wage.
Conclusion
Given the generation-long stagnation of the pre-tax incomes among the bottom 50 percent of wage earners in the United States, we feel that the policy discussion at the federal, state, and local levels should focus on how to equalize the distribution of human capital, financial capital, and bargaining power rather than merely the redistribution of national income after taxes. Policies that could raise the pre-tax incomes of the bottom 50 percent of income earners could include:
- Improved education and access to skills, which may require major changes in the system of education finance and admission
- Reforms of labor market institutions to boost workers’ bargaining power and including a higher minimum wage
- Corporate governance reforms and worker co-determination of the distribution of profits
- Steeply progressive taxation that affects the determination of pay and salaries and the pre-tax distribution of income, particularly at the top end
The different levels of government in the United States today obviously have the power to make income distribution more unequal, but they also have the power to make economic growth in America more equitable again. Potentially pro-growth economic policies should always be discussed alongside their consequences for the distribution of national income and concrete ways to mitigate their unequalizing effects. We hope that the distributional national accounts we present today can prove to be useful for such policy evaluations.
We will post online our complete distributional national accounts micro-data. These micro-files make it possible for researchers, journalists, policymakers, and any interested user to compute a wide array of distributional statistics—income, wealth, taxes paid and transfers received by age, gender, marital status, and other measures—and to simulate the distributional consequences of tax and transfer reforms in the United States.