From David Ruccio The premise and promise of capitalism, going back to Adam Smith, have been that global wealth would increase and serve as a benefit to all of humanity.* But the experience of recent decades has challenged those claims: while global wealth has indeed grown, most of the increase has been captured by a small group at the top. The result is that an obscenely unequal distribution of the world’s wealth has become even more unequal—and, if business as usual continues, it will turn out to be even more grotesquely unequal in the decades ahead. The alarm was most recently sounded by Michael Savage, in the Guardian, who cited a projection produced by the House of Commons library to the effect that, if trends seen since the 2008 financial crash were to continue, then the top 1%
Topics:
David F. Ruccio considers the following as important: Uncategorized
This could be interesting, too:
tom writes The Ukraine war and Europe’s deepening march of folly
Stavros Mavroudeas writes CfP of Marxist Macroeconomic Modelling workgroup – 18th WAPE Forum, Istanbul August 6-8, 2025
Lars Pålsson Syll writes The pretence-of-knowledge syndrome
Dean Baker writes Crypto and Donald Trump’s strategic baseball card reserve
from David Ruccio
The premise and promise of capitalism, going back to Adam Smith, have been that global wealth would increase and serve as a benefit to all of humanity.* But the experience of recent decades has challenged those claims: while global wealth has indeed grown, most of the increase has been captured by a small group at the top. The result is that an obscenely unequal distribution of the world’s wealth has become even more unequal—and, if business as usual continues, it will turn out to be even more grotesquely unequal in the decades ahead.
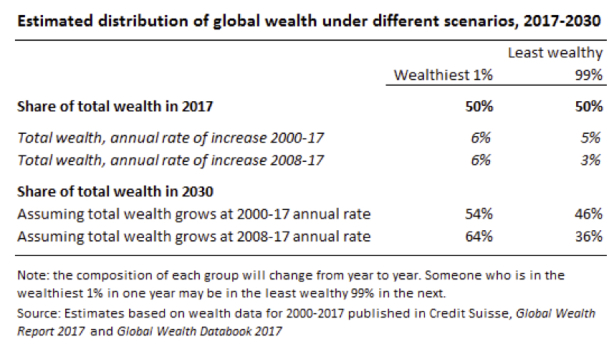
The alarm was most recently sounded by Michael Savage, in the Guardian, who cited a projection produced by the House of Commons library to the effect that, if trends seen since the 2008 financial crash were to continue, then the top 1% will hold 64% of the world’s wealth by 2030.”
I finally managed to track down that report, which was commissioned by MP Liam Byrne, who is the chair of the All-Party Parliamentary Group on Inclusive Growth. It relies on data compiled by Credit Suisse and a projection assuming that total wealth grows at the same rates as during the period 2008-17.
The problem, of course, is global wealth is notoriously difficult to calculate—for both empirical and theoretical reasons—and Credit Suisse doesn’t reveal its methodology.
That’s why the work of the World Inequality Lab is so important.** They’re doing the painstaking work of calculating the wealth that has been generated by global capitalism and how its ownership is distributed.
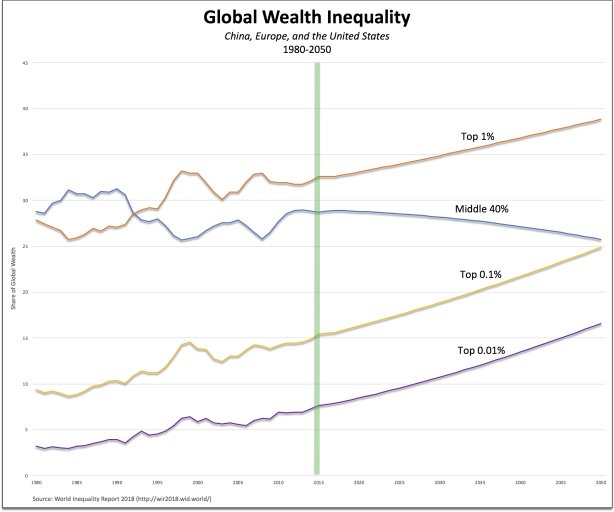
Thus far, they have reasonably good data for a selection of nations: China, Europe (represented by three countries, France, Spain, and the United Kingdom), and the United States. Those are the numbers illustrated in the chart at the top of this post (with the vertical green line, at 2015, separating past trends from future projections). What they find is that
At the global level represented by China, Europe, and the United States), wealth is substantially more concentrated than income: the top 10% owns more than 70% of the total wealth. The top 1% wealthiest individuals alone own 33% of total wealth in 2017. This figure is up from 28% in 1980. The bottom of the population, on the other hand, owns almost no wealth over the entire period (less than 2%).
The share owned by the top 1 percent is less than reported by Byrne but it’s still an one-third of global wealth. (The share for the top 1 percent in the United States is even higher: an astounding 41.8 percent in 2012.)
But the projection looking forward is similarly dramatic: according to the World Inequality Lab, if present trends continue the share of each of the top groups—the top 1 percent, the top 0.1 percent, and the top 0.01 percent—would growth by one percentage point every five years. What that means is that, by 2050, the share of each group would increase dramatically. In particular, the share owned by the top 0.1 percent would eventually match that of the declining middle group—at a quarter of global wealth.
What we’ve been seeing in recent decades is that an unequal distribution of wealth leads to even more inequality, since wealth inequality is amplified as wealth is concentrated in the hands of a small group at the top. First, past wealth is capitalized at a faster pace, since the rate of return on wealth is faster than the rate of growth of the economy. Moreover, this effect is reinforced by the fact that rates of return tend to increase with the level of wealth: the rates of return available to large financial portfolios are usually much higher than those open to small bank deposits and the other savings vehicles available to everyone else.
None of this is new. Those in the small group at the top have long been able to put distance between themselves and everyone else precisely because they’ve been able to capture the surplus and then convert their share of the surplus into ownership of wealth. And the returns on their wealth allow them to capture even more of the surplus produced within global capitalism.
In short, unless radical economic changes are made within nations, the unequal distribution of global wealth created by contemporary capitalism is both the premise and promise of an even more unequal distribution of wealth in the decades to come.
*To be clear, the “wealth of nations” that Smith referred to was current production or, as it is currently measured, Gross Domestic Product—the “immense accumulation of commodities” produced and exchanged in a country’s economy over a particular period of time. Mainstream economists (such as Robert Barro) often claim that inequality in global capitalism is decreasing, because of “convergence,” that is, growth rates in developing countries of the Global South are faster than in the developed North and the gap in GDP per capita is closing. Today, wealth refers to the ownership of assets, both financial (stocks, bonds, etc.) and nonfinancial (especially housing)—as against income (flows of value associated with either doing or owning) or sums of transactions (which is what is captured in GDP).
**The other major sources of information on global wealth are Forbes (which publishes global rankings on the world’s billionaires) and the French business consulting company Capgemini (which issues an annual World Wealth Report focused on the wealth of global High Net Worth Individuals).