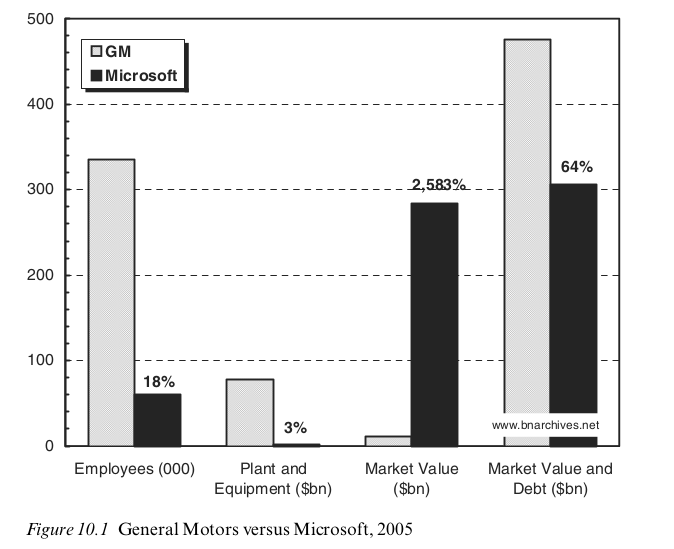
Source: Nitzan and Bichler, Capital as Power In 2005, Microsoft’s market value was 2,583% greater than that of General Motors. Mainstream economists would say that Microsoft therefore had more property than GM. But more of what? Nitzan and Bichler point out that when we look under the hood of market value, there’s nothing ‘real’ to back it up. Microsoft, for instance, has only 18% as many employees as GM. And it owns only 3% as much equipment (in dollar terms). So is this a distortion? Is it a sign that Microsoft’s wealth is fictitious? No, say Nitzan and Bichler. Wealth isn’t about material property. Instead, they argue that wealth is a commodification of property rights. So Microsoft’s greater market value stems from its greater ability to convert property rights into income.
Topics:
Editor considers the following as important: Uncategorized
This could be interesting, too:
tom writes The Ukraine war and Europe’s deepening march of folly
Stavros Mavroudeas writes CfP of Marxist Macroeconomic Modelling workgroup – 18th WAPE Forum, Istanbul August 6-8, 2025
Lars Pålsson Syll writes The pretence-of-knowledge syndrome
Dean Baker writes Crypto and Donald Trump’s strategic baseball card reserve
Source: Nitzan and Bichler, Capital as Power
In 2005, Microsoft’s market value was 2,583% greater than that of General Motors. Mainstream economists would say that Microsoft therefore had more property than GM. But more of what? Nitzan and Bichler point out that when we look under the hood of market value, there’s nothing ‘real’ to back it up. Microsoft, for instance, has only 18% as many employees as GM. And it owns only 3% as much equipment (in dollar terms).
So is this a distortion? Is it a sign that Microsoft’s wealth is fictitious? No, say Nitzan and Bichler. Wealth isn’t about material property. Instead, they argue that wealth is a commodification of property rights. So Microsoft’s greater market value stems from its greater ability to convert property rights into income. That Microsoft can do this without owning bricks and mortar is interesting, but not surprising. As intellectual property teaches us, property rights need not be attached to anything physical.