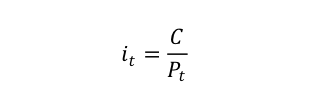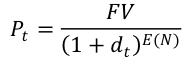New legislation calling on the USPS to begin offering banking services is a dangerous use of government resources. Not just payday lenders that are whining. American Banker — Bank ThinkPostal banking should be a dead letter Rebeca Romero Rainey | President and CEO of Independent Bankers of America
Read More »Lars P. Syll — How money is created
David Graeber and the Bank of England. Lars P. Syll’s BlogHow money is createdLars P. Syll | Professor, Malmo University
Read More »Money and Banking Post 21: The Interest Rate
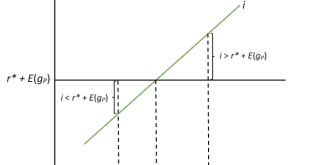
By Eric Tymoigne In Post 20, a lot is said about the role that the rate of return on financial instruments—the interest rate—plays on the pricing on securities, but little was said about what determines that rate of return. Two competing theoretical frameworks explain what influences the interest rate, one of them emphasizes the role of real factors and the other emphasizes monetary factors. Real Theory of Interest Rate: Natural Interest Rate and Expected Inflation Gross Substitution and...
Read More »Money and Banking Post 20: Pricing Securities
A Small Detour: Savings Account and Interest Compounding A typical way to think about interest rates is to study how a savings account works. Suppose Mr. X puts $1000 in a savings account that provides a one percent annual interest rate. In that case, X will get at the end of: Year 1: $1010 = $1000(1 + 0.01) Year 2: $1020.1 = $1010(1 + 0.01) = $1000(1.01)2 … Year 5: $1051.01 = $1000(1.01)5 Several things are worth noticing: The rate of return is fixed by the issuer of the account (1%)...
Read More »Money and Banking – Part 19 (A): Financial institutions: An overview
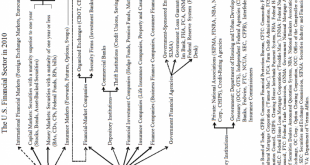
Part A | Part B | Part C Erratum on Post 18: Figure 18.10 has reversed proportions: about 30 percent are issued by nonfinancial corporations. Note: As I was afraid it would happen, someone emailed me to take issue with the way I use the term promissory note. “Promissory note” has a specific meaning in the law—it is a specific type of financial instruments—but Post 18 uses the term conceptually to mean any formal promise made by someone—a synonymous to financial instrument—, which may...
Read More »Money and Banking – Part 19 (B): Financial institutions: An overview
Part A | Part B | Part C Regulated Portfolio Management Companies: Mutual Funds and Others Portfolio management companies provide a wide variety of placement opportunities to economic units with spare funds who do not want to, or cannot, directly buy securities or other assets. There are three broad types of portfolio management companies: mutual funds, closed-end funds, and unit investment trusts (UITs). One of the main differences between them is the characteristics of the shares...
Read More »Money and Banking – Part 19 (C): Financial institutions: An overview
Part A | Part B | Part C Farmer Mac, Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, and Sallie Mae This section closes the presentation of government-sponsored enterprise with a quick look at other GSEs. They work in a similar fashion to the FCS, by issuing securities and using the proceeds to buy or to back illiquid financial instruments held by financial institutions. The goal is once again to lower the level and volatility of interest rates on specific financial instruments and to encourage credit for...
Read More »Money and Banking—Part 18 (B): Overview of the Financial System: A World of Promises
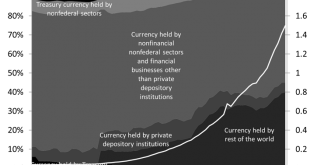
Due to the size of this post, it has been split into 2. You can find part A here. Monetary instruments Monetary instruments are the last type of marketable promissory notes. Post 15 and Post 16 are devoted to their analysis. One of the main characteristics of monetary instruments is that their term to maturity is instantaneous, that is, they can be returned to the issuer at the will of the bearer. In terms of cash, that is physical monetary instruments, the Financial Accounts of the...
Read More »Money and Banking—Part 18 (A): Overview of the Financial System: A World of Promises
Due to the size of this post, it was split in two. You can find Part B here. The M&B series is back! The goal is to finish the first complete draft of the book by the time I need to teach my Money and Banking course. Over the coming months, the following topics will be covered. Overview of the financial system Federal Reserve System institutional analysis Interest rate and interest rate structure Pricing of securities Off balance sheet: Securitization Off balance sheet: Derivatives...
Read More »Money and Banking Part 17: History of Monetary Systems
By Eric Tymoigne This is the last post of this series. Many more topics need to be covered to make a full Money and Banking course, but the series should help those of us who are dissatisfied with the current Money & Banking textbooks (I don’t use any). Here is what is coming up in the near future: I will edit all the posts for typos (most of them hopefully) and to account for comments I received. Devin Smith kindly agreed to post the changes without changing any of the links....
Read More » Heterodox
Heterodox