Q1 Senior Loan Officer Survey: strong demand for loans, but accommodation ends The Senior Loan Officer Survey for Q1 was published yesterday (May 10), generally covering the supply of, and demand for, bank credit. It has two components that qualify as long leading indicators for the economy, as they have typically turned about one year before the onset of a recession over their 30+ year history. First, the below graph is of the percentage of banks tightening standards for commercial and industrial loans for large and medium-sized firms (blue) and small firms (red). Since tightening constricts credit, it typically happens in advance of a recession. Thus a positive number in the below graph is a negative for the economy: As you can see,
Topics:
NewDealdemocrat considers the following as important: Senior Loan Officer Survey, US EConomics
This could be interesting, too:
NewDealdemocrat writes JOLTS revisions from Yesterday’s Report
Bill Haskell writes The North American Automobile Industry Waits for Trump and the Gov. to Act
Bill Haskell writes Families Struggle Paying for Child Care While Working
Joel Eissenberg writes Time for Senate Dems to stand up against Trump/Musk
Q1 Senior Loan Officer Survey: strong demand for loans, but accommodation ends
The Senior Loan Officer Survey for Q1 was published yesterday (May 10), generally covering the supply of, and demand for, bank credit. It has two components that qualify as long leading indicators for the economy, as they have typically turned about one year before the onset of a recession over their 30+ year history.
First, the below graph is of the percentage of banks tightening standards for commercial and industrial loans for large and medium-sized firms (blue) and small firms (red). Since tightening constricts credit, it typically happens in advance of a recession. Thus a positive number in the below graph is a negative for the economy:
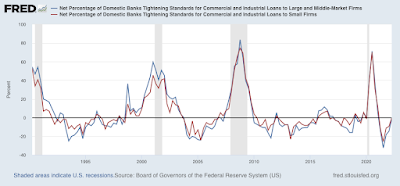
As you can see, these moved towards absolute neutrality in the first quarter. In fact, the reading as to small firms is exactly 0, while that as to larger firms is -1.5, indicating a very slight tilt towards loosening.
Next, below is the percentage of banks reporting increasing demand for loans by larger (blue) and smaller (red) firms. In this case, more demand indicates a desire to build and expand on the part of firms, so a positive reading is also a positive for the economy:
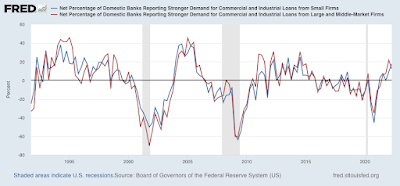
Demand remains quite strong for both sized firms.
The survey includes a large number of other measures, but these are either too noisy, not very predictive, or of too recent a vintage (10 years or less) to be of much use.
The two above series together make for a weak positive. Demand for loans is still quite strong, but standards have stopped moving towards accommodation.
Note that the Chicago Financial Indexes measure credit conditions as well, but have the advantage of being reported weekly rather than once every three months. Interestingly, both the adjusted and leverage indexes significantly deteriorated just since the Fed started raising rates over a month ago. Below I include those two measures compared with the percentage of banks tightening standards for large firms (as above) for comparison:
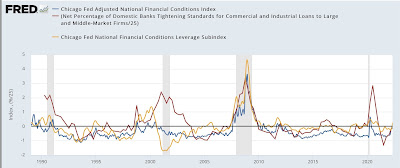
It would not be surprising at all for next Quarter’s senior loan officer survey to cross the threshold into negative territory – but it’s not there yet.
