Just like American companies, Volkswagen made the jump to EVs the technology of which is still being developed and just before the pandemic. Of course, the pandemic created an economic desert where people cut buying anything other than essentials. Fewer vehicles sold leads to an abundance of uncovered costs and debt. Can’t reduce the costs of a fixed asset such as a plant producing the vehicles. The next place to look for cost reduction is Labor. And that is where the battle is going as reported by WSJ. Volkswagen Labor is not too happy with the VW Volkswagen CEO Oliver Blume who is suggesting cuts in Labor. Oliver Blume replaced CEO Herbert Diess who made the decision to move to EV technology and retired with a nice pension. Just like American
Topics:
Bill Haskell considers the following as important: US/Global Economics, VW EVs
This could be interesting, too:
Joel Eissenberg writes How Tesla makes money
Angry Bear writes True pricing: effects on competition
Angry Bear writes The paradox of economic competition
Angry Bear writes USMAC Exempts Certain Items Coming out of Mexico and Canada
Just like American companies, Volkswagen made the jump to EVs the technology of which is still being developed and just before the pandemic. Of course, the pandemic created an economic desert where people cut buying anything other than essentials. Fewer vehicles sold leads to an abundance of uncovered costs and debt. Can’t reduce the costs of a fixed asset such as a plant producing the vehicles. The next place to look for cost reduction is Labor. And that is where the battle is going as reported by WSJ.
Volkswagen Labor is not too happy with the VW Volkswagen CEO Oliver Blume who is suggesting cuts in Labor. Oliver Blume replaced CEO Herbert Diess who made the decision to move to EV technology and retired with a nice pension. Just like American automakers are finding, the technology to make the EVs is still being created and there are unplanned increasing costs from manufacturing. Couple such with a pandemic and Volkswagen is underperforming in the profit margin are.
Volkswagen like other automakers, quickly took on the EV manufacture probably believing they would have new technology along the way or improve the present technology. Neither has come about. Maybe they should have stuck with hybrids for a while longer and let the others blaze the path. It is not like people are dissing hybrids. Indeed, they are embracing hybrids as the EV support technology in the manner o charging stations and quick charging is still not in abundance.
Of course, the gamble was made worse by a long-term pandemic. WSJ has a good take on both issues.
For Volkswagen, the Bumpy Road to Electric Vehicles Starts to Hit Home
Volkswagen suggests it might have to close a plant in Germany for the first time ever. This sets up a battle with its powerful union and highlights the mounting pressures on its namesake brand.
The carmaker’s bosses raised the prospect of a plant closure last week Monday as it navigates an increasingly bumpy transition toward electric vehicles. The company said a “performance program” at its core Volkswagen brand agreed upon with union leaders last December would no longer be sufficient to hit profit targets, following a disappointing first half of the year. Chief Executive Oliver Blume said in a statement:
“The economic environment became even tougher, and new competitors are entering the European market.”
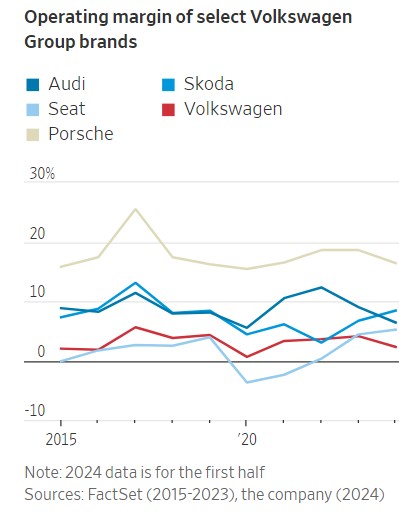
The Volkswagen brand, the group’s largest in terms of sales, contributed less than 1/10th of total operating profit in the first half. Its margin was just 2.3%, or 3.6% excluding the costs of a severance program.
On Wednesday, Volkswagen management held a high-stakes meeting with employees at a vast hall within its Wolfsburg headquarters to give further details of the new savings plan.
Group Chief Financial Officer Arno Antlitz blamed the poor result squarely on the poor post pandemic recovery. “In Europe, two million fewer vehicles are currently sold than before Covid,” he said.
However, a big bet on electric vehicles under former CEO Herbert Diess with products such as the ID.3 and ID.4 is another reason for today’s weak profitability, according to analysts.
“There are plants dedicated to EVs that aren’t producing at the levels expected and costs are out of whack,” said Bernstein analyst Stephen Reitman.
A few days before Volkswagen announced its December deal with the union, the German government unexpectedly canceled EV subsidies. The technology has struggled to win over fresh cohorts of buyers who may be wary of patchy public charging infrastructure and higher prices.
EV sales in Germany, where Volkswagen is the market leader, fell by a fifth in the year through July, compared with the same period of 2023.
To get the Volkswagen brand’s finances back on track, managers want to take more radical steps than were possible under the previous union deal, notably ending an agreement to rule out compulsory redundancies that has been in place since 1994.
Daniela Cavallo, the union leader who heads Volkswagen’s works council, has vowed to fight the move, which is a prerequisite for any potential plant closure in Germany
“Volkswagen’s ailment isn’t German plants or staffing costs; it is that management isn’t doing its job,” Cavallo told Wednesday’s employee meeting, according to prepared remarks of a speech streamed live by local media.
In an earlier interview with the company’s union newspaper, Cavallo blamed the brand’s poor performance on management missteps such as Diess’s dismissal of hybrids as a niche technology. Car buyers this year have gravitated toward hybrids as a way to get better fuel economy without the charging hassle and expense of an EV.
Underscoring the trend, Sweden’s Volvo Car separately Wednesday abandoned its target of having a fully electric lineup by the end of the decade, saying it was still likely to sell some hybrid models.
The face-off at Volkswagen is already attracting scrutiny in Berlin. On Tuesday, Germany’s economy and climate-protection minister, Robert Habeck, called for long-term thinking and “close coordination with social partners” at Volkswagen. He said the government was preparing tax relief for EVs as part of a new growth plan.
Volkswagen can’t easily dial back its profit-sapping EV investments or production because its cars need to meet much stricter European emissions standards starting next year. Its fleet carbon emissions last year were 24.2% higher than they will need to be in 2025, according to data collated by Bernstein, compared with 19.6% for Mercedes-Benz and 9.7% for BMW.
The company also needs to compete with lower-cost, faster-moving Chinese EV makers, not just in China but increasingly in Europe too. Chinese manufacturers have a cost advantage of as much as 30%, according to industry estimates.
In the first half of this year, Volvo Car’s made-in-China EX30 overtook Volkswagen’s ID.3 and ID.4 in Europe’s EV sales rankings, according to data provider JATO Dynamics.
BYD, the Chinese brand that last year overtook Volkswagen in China, is still a marginal player in Europe, but it is growing fast and spending lavishly. This summer it sponsored the high-profile Euro 2024 soccer tournament and last week agreed to buy its German distributor.
While Volkswagen’s profitability in the first half was particularly weak, its performance has long been a drag on the group, which also includes lucrative luxury marques such as Porsche and Audi.
Other mass-market brands owned by the group, such as Skoda and SEAT, based in the Czech Republic and Spain, respectively, have reported higher margins than Volkswagen itself in recent years.
In his statement, Blume noted that “Germany in particular as a manufacturing location is falling further behind in terms of competitiveness.”
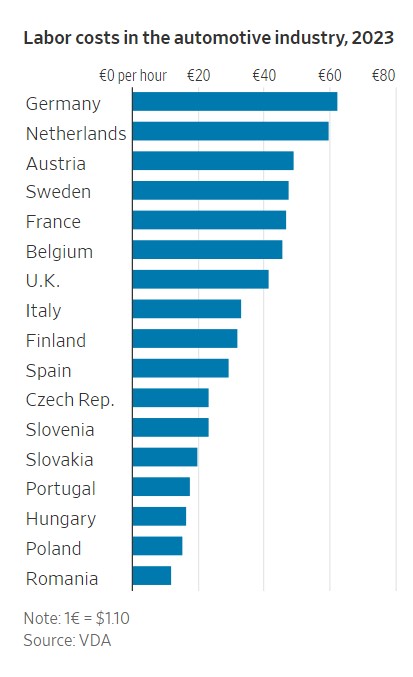
Labor costs in Germany are the highest in Europe, according to an analysis by the German Association of the Automotive Industry. A German auto worker cost roughly €62 an hour last year—equivalent to roughly $68.50—compared with €23 for a Czech worker and €29 for a Spanish one. In Hungary, where BYD is building a factory to avoid European Union tariffs, auto workers are paid only €16 an hour.
Germany’s energy costs also have risen since the country lost access to cheap Russian pipeline gas as a result of the war in Ukraine.
Volkswagen has a long history of resisting redundancies. In 1993, when the company was losing money in an economic slump, its management and union agreed to a four-day week as an alternative to a plan involving 30,000 job cuts.
Veteran German stock analyst Jürgen Pieper expects the latest war of words that has broken out between Volkswagen’s management and union to end in some kind of compromise that again avoids closing plants. One option could be the sale of components businesses, he said.
“The challenge for management is that this isn’t a full-scale crisis. Volkswagen just gets a little weaker every year.”