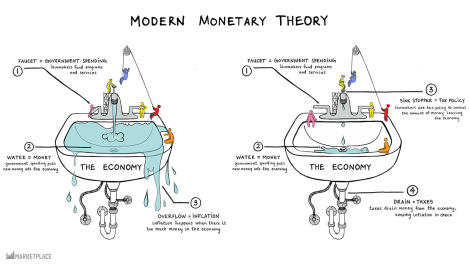
From Lars Syll Whether it’s more nurses, frozen tax promises, free broadband internet or more social housing in the UK; or tax cuts and green energy investments in America, public spending is set to surge. This sudden abandonment of fiscal rectitude comes amid the rise in prominence of a way of thinking about money, spending and the economy – Modern Monetary Theory (MMT). According to its key architect, US businessman Warren Mosler, it is based on a simple idea – that countries that issue their own currencies can never run out of money in the same way a business or person can. This is important to understand because it means when someone says the government can’t do something for want of money, that’s simply not applicable, says Mr Mosler. A government can no more run out of money
Topics:
Lars Pålsson Syll considers the following as important: Uncategorized
This could be interesting, too:
tom writes The Ukraine war and Europe’s deepening march of folly
Stavros Mavroudeas writes CfP of Marxist Macroeconomic Modelling workgroup – 18th WAPE Forum, Istanbul August 6-8, 2025
Lars Pålsson Syll writes The pretence-of-knowledge syndrome
Dean Baker writes Crypto and Donald Trump’s strategic baseball card reserve
from Lars Syll
Whether it’s more nurses, frozen tax promises, free broadband internet or more social housing in the UK; or tax cuts and green energy investments in America, public spending is set to surge. This sudden abandonment of fiscal rectitude comes amid the rise in prominence of a way of thinking about money, spending and the economy – Modern Monetary Theory (MMT).
According to its key architect, US businessman Warren Mosler, it is based on a simple idea – that countries that issue their own currencies can never run out of money in the same way a business or person can. This is important to understand because it means when someone says the government can’t do something for want of money, that’s simply not applicable, says Mr Mosler. A government can no more run out of money than a football stadium can run out of goals scored …
MMTers say they do believe in being fiscally responsible, and that critics misunderstand. The story starts with any government’s desire to fund public services, which it does through taxation. Citizens need money to pay that tax, and they work to get it, Mr Mosler says …
The tax-and-spend orthodoxy embraced by most governments should be rethought. What’s actually going on is tax liabilities come first, then spending, and then payment of taxes, which paints guiding economic principles such as the debt and deficit in entirely different lights.
In modern times legal currencies are based on fiat. Currencies no longer have intrinsic value (as gold and silver). What gives them value is basically the simple fact that you have to pay your taxes with them. That also enables governments to run a kind of monopoly business where it never can run out of money. A fortiori, spending becomes the prime mover and taxing and borrowing is degraded to following acts. If we have a depression, the solution, then, is not austerity. It is spending. Budget deficits are not a major problem since fiat money means that governments can always make more of them.
In the mainstream economist’s world, we don’t need fiscal policy other than when interest rates hit their lower bound (ZLB). In normal times monetary policy suffices. The central banks simply adjust the interest rate to achieve full employment without inflation. If governments in that situation take on larger budget deficits, these tend to crowd out private spending and the interest rates get higher.
What mainstream economists have in mind when they argue this way, is nothing but a version of Say’s law, basically saying that savings have to equal investments and that if the state increases investments, then private investments have to come down (‘crowding out’). As an accounting identity, there is, of course, nothing to say about the law, but as such, it is also totally uninteresting from an economic point of view. What happens when ex-ante savings and investments differ, is that we basically get output adjustments. GDP changes and so makes saving and investments equal ex-post. And this, nota bene, says nothing at all about the success or failure of fiscal policies!
It is true that MMT rejects the traditional Phillips curve inflation-unemployment trade-off and has a less positive evaluation of traditional policy measures to reach full employment. Instead of a general increase in aggregate demand, it usually prefers more ‘structural’ and directed demand measures with less risk of producing increased inflation. At full employment deficit spendings will often be inflationary, but that is not what should decide the fiscal position of the government. The size of public debt and deficits is not — as already Abba Lerner argued with his ‘functional finance’ theory in the 1940s — a policy objective. The size of public debt and deficits are what they are when we try to fulfill our basic economic objectives — full employment and price stability.
That governments can spend whatever amount of money they want is a fact. That does not mean that MMT says they ought to — that’s something our politicians have to decide. No MMTer denies that too much of government spendings can be inflationary. What is questioned is that government deficits necessarily is inflationary.