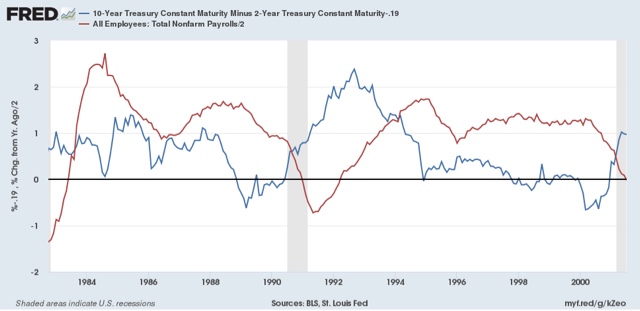
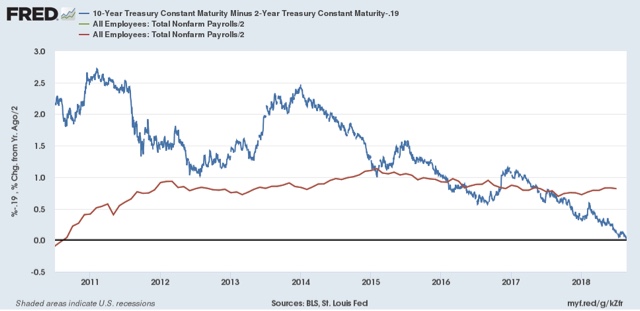
What the compressed yield curve means for employment Aside from the threat of a recession down the road, is there cause for concern by economic Progressives in the fact that the yield curve has tightened (i.e., the difference in interest rates between long and short term bonds has become very small)? In a word, Yes. Four times during the 1980s and 1990s the difference in the interest yield between 2 and 10 year treasury bonds got about as low as it is now (blue in the graphs below). That occurred in 1984, 1986, 1994, and 1998. Even though on none of those 4 occasions a recession followed, on 3 of 4 of those occasions YoY employment gains (red, divided by 2 for scale) subsequently declined: In both 1984 and 1994, YoY employment gains peaked
Topics:
NewDealdemocrat considers the following as important: Taxes/regulation, US/Global Economics
This could be interesting, too:
Joel Eissenberg writes How Tesla makes money
Angry Bear writes True pricing: effects on competition
Angry Bear writes The paradox of economic competition
Angry Bear writes USMAC Exempts Certain Items Coming out of Mexico and Canada
What the compressed yield curve means for employment
Aside from the threat of a recession down the road, is there cause for concern by economic Progressives in the fact that the yield curve has tightened (i.e., the difference in interest rates between long and short term bonds has become very small)?
In a word, Yes.
Four times during the 1980s and 1990s the difference in the interest yield between 2 and 10 year treasury bonds got about as low as it is now (blue in the graphs below). That occurred in 1984, 1986, 1994, and 1998.
Even though on none of those 4 occasions a recession followed, on 3 of 4 of those occasions YoY employment gains (red, divided by 2 for scale) subsequently declined:
In both 1984 and 1994, YoY employment gains peaked within 2 months of the low point in the yield spread. In the 1980s, that decline continued right through and a little beyond the 1986 low in spreads. In both cases YoY gains in employment declined by roughly half. Only in 1998 was there no appreciable effect.
In other words, even if the Fed stops raising rates now, and the yield curve does not get tighter or fully invert, my expectation is that monthly employment gains will decline to about half of what they have recently been — i.e., to about 100,000 a month — during the next year or so.