July inflation consistent with early recovery; no compelling evidence of wage deflation Yesterday morning July consumer prices were reported to have increased 0.6% for the second month in a row (as did core inflation, ex-food and energy): As a result, YoY inflation has increased to 1.0%: The widespread price increases are signs of increased demand, which in these circumstances is a good thing. In the past, deflationary recessions, most notably the “great contraction” of 1929-32, ended when the YoY change in producer and consumer prices bottomed out. In this recession they did so in April, so this adds to the evidence that *technically* a recovery has been in progress thereafter (even though in absolute terms things remain awful. They are simply
Topics:
NewDealdemocrat considers the following as important: politics, Taxes/regulation, US/Global Economics
This could be interesting, too:
Robert Skidelsky writes Lord Skidelsky to ask His Majesty’s Government what is their policy with regard to the Ukraine war following the new policy of the government of the United States of America.
Joel Eissenberg writes No Invading Allies Act
Ken Melvin writes A Developed Taste
Bill Haskell writes The North American Automobile Industry Waits for Trump and the Gov. to Act
July inflation consistent with early recovery; no compelling evidence of wage deflation
Yesterday morning July consumer prices were reported to have increased 0.6% for the second month in a row (as did core inflation, ex-food and energy):
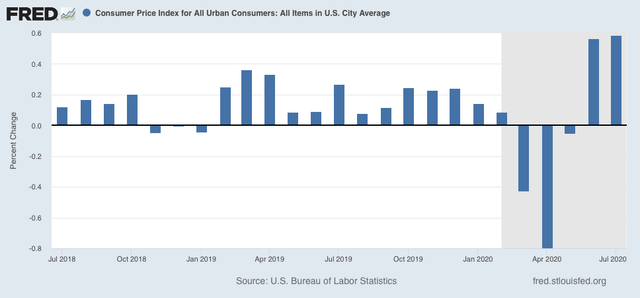
As a result, YoY inflation has increased to 1.0%:
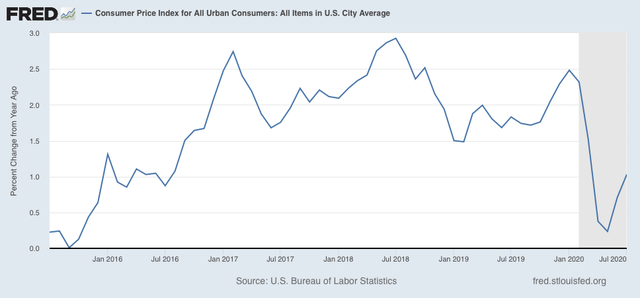
The widespread price increases are signs of increased demand, which in these circumstances is a good thing. In the past, deflationary recessions, most notably the “great contraction” of 1929-32, ended when the YoY change in producer and consumer prices bottomed out. In this recession they did so in April, so this adds to the evidence that *technically* a recovery has been in progress thereafter (even though in absolute terms things remain awful. They are simply “less awful” than before).
Because I have been looking for signs of wage deflation, let’s put this morning’s inflation data into the mix.
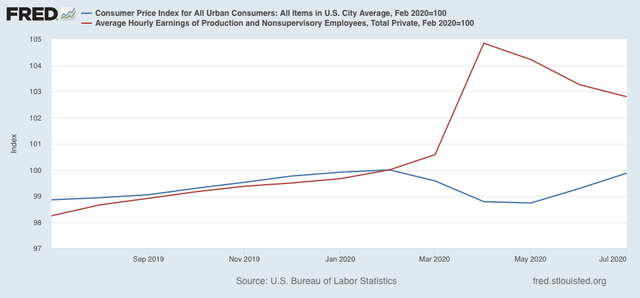
Remember that *average* wages increased because the vast majority of workers laid off during the lockdowns were in low-wage jobs. Relatively speaking, the remaining workforce therefore consisted of higher-paid workers.
Typically in recoveries hours are added before jobs. That has been the case since April. Aggregate hours (red in the graph below) have rebounded by slightly more than 50% from their February through April losses, while jobs (blue) have only made back 42% of their decline. As a result, aggregate payrolls (green) have increased faster than jobs:
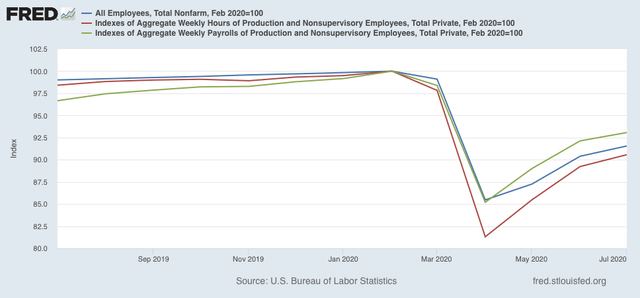
In short, the inflation and jobs picture are what we would typically expect as a recovery is starting out. Although there were lots of anecdotes about pay cuts early in the pandemic, so far it is not showing up in any compelling way in the data (which is definitely a *good* thing).
Whether the recovery will continue, of course, is completely contingent on the future course of the pandemic.
