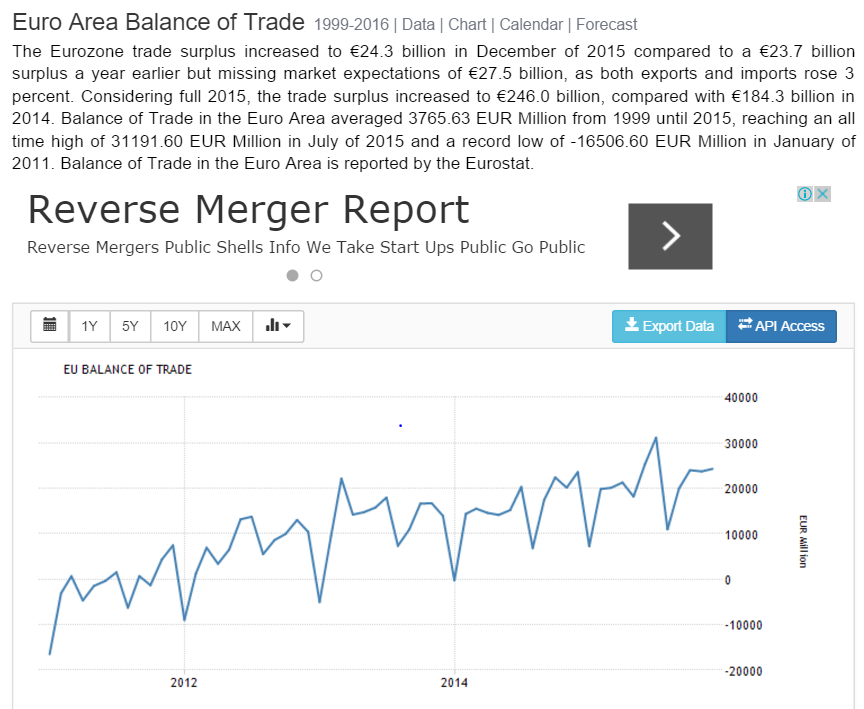
A lot worse than expected and still deep in contraction: Empire State Mfg SurveyHighlightsFor the seventh straight month, the Empire State report is signaling significant contraction for the manufacturing sector. The general business conditions index for February came in below low-end expectations, at minus 16.64 vs even deeper contraction of minus 19.37 in January. New orders, at minus 11.63, are in contraction for a ninth month in a row while employment, though improving to minus 0.99 from minus 13.00, is in contraction for an eighth month in a row.Shipments are in contraction at minus 11.56 with unfilled orders at minus 6.93. The workweek is at minus 5.94. One reading in the plus column is the six-month outlook, up nearly 5 points to 14.48 which, however, is unusually low for this reading which usually tracks in the 30s and 40s. Price data show marginal improvement for inputs but contraction for finished goods.This report is showing its weakest run by far of the recovery and, unfortunately, points to extended weakness for the nation’s factory which is getting hit by weak exports and weak energy markets at home.
Topics:
WARREN MOSLER considers the following as important: China, Comodities, currencies, housing
This could be interesting, too:
Nick Falvo writes Subsidized housing for francophone seniors in minority situations
NewDealdemocrat writes Declining Housing Construction
Nick Falvo writes Homelessness among older persons
Dean Baker writes Donald Trump is badly nonfused # 67,218: The story of supply and demand
A lot worse than expected and still deep in contraction:
Empire State Mfg Survey
Highlights
For the seventh straight month, the Empire State report is signaling significant contraction for the manufacturing sector. The general business conditions index for February came in below low-end expectations, at minus 16.64 vs even deeper contraction of minus 19.37 in January. New orders, at minus 11.63, are in contraction for a ninth month in a row while employment, though improving to minus 0.99 from minus 13.00, is in contraction for an eighth month in a row.Shipments are in contraction at minus 11.56 with unfilled orders at minus 6.93. The workweek is at minus 5.94. One reading in the plus column is the six-month outlook, up nearly 5 points to 14.48 which, however, is unusually low for this reading which usually tracks in the 30s and 40s. Price data show marginal improvement for inputs but contraction for finished goods.
This report is showing its weakest run by far of the recovery and, unfortunately, points to extended weakness for the nation’s factory which is getting hit by weak exports and weak energy markets at home.
This is going the wrong way for what’s been promoted as the ‘driver’ of the economy for the year:
Housing Market Index
Highlights
Optimism among home builders is cooling noticeably, based on the housing market index for February which is down 3 points to 58 for the lowest reading since May last year. But 58 is still well over breakeven 50 with the future sales component actually rising 1 point to 65. The current sales component, however, is down 3 points to 65 which points to expected slowing for tomorrow’s starts & permits data. The traffic component has been holding down this report throughout the whole recovery and continues to do so, down a steep 5 points to 39 and the lowest reading since also May last year. Weakness here reflects lack of first-time buyers and also perhaps the major snowstorm that hit the East Coast at mid-month.Details show step backwards for all four regions with the West, a key region for the new home sector, down 5 points to a still standout composite score of 68. The South and Midwest are both at 57 with the Northeast continuing to trail far behind, down 2 points to 45.
Builders are citing scarcity of both labor and available lots as negatives right now. Momentum in the housing sector was bumpy last year and, based on this report, looks to remain so, at least through the early part of this year.
As previously discussed, not good for bank, either:
High risk of bankruptcy for one-third of oil firms: Deloitte
Feb 16 (Reuters) — Roughly a third of oil producers are at high risk of slipping into bankruptcy this year as low commodity prices crimp their access to cash and ability to cut debt, according to a study by Deloitte. The report is based on a review of more than 500 publicly traded oil and natural gas exploration and production companies across the globe. The roughly 175 companies at risk of bankruptcy have more than $150 billion in debt, with the slipping value of secondary stock offerings and asset sales further hindering their ability to generate cash, Deloitte said in the report.
Pro active currency depreciation tends to have these kinds of consequences:
Japan’s household spending falls 2.7% in 2015
Feb 16 (Kyodo) — Japan’s average monthly household spending in 2015 fell 2.7 percent in price-adjusted real terms from the previous year to 247,126 yen for the second straight year of decrease. The drop followed a demand surge in the January to March period in 2014 before the consumption tax increase in April as well as weak sales of clothing due to an unusually warm winter, according to an official of the Internal Affairs and Communications Ministry. The decline compares with a 3.2 percent drop in 2014. Household spending figures are a key indicator of private spending, which accounts for around 60 percent of the nation’s gross domestic product.
Two things. First, weak exports tend to reflect weak global demand. Second, reduced imports tend to reflect weak domestic demand.
And the ‘solid’ -;)- trade surplus is a fundamental force that works to support the currency:
China Trade Surplus Hits Fresh Record High in January
China trade surplus stood at USD63.29 billion in January of 2016, widening from USD60.03 billion reported a year earlier and beating market consensus. It is the largest trade surplus on record, as exports and imports fell far worse than expected. In January, exports plunged by 11.2 percent year-on-year to USD177.48 billion, following a 1.4 percent fall in December 2015.Imports tumbled by 18.8 percent year-on-year to USD114.19 billion, following a 7.6 percent decline in the preceding month, the 14th straight month of contraction, as a result of declining commodity prices and weak demand.
Same for the euro: