In the U.S., we are told, the post-World War II period was a golden age of full employment. High wartime government spending had brought to an end the double-digit unemployment and misery of the Depression, and as war gave way to peace, unemployment settled at a non-inflationary level of 3-5%. It's known as the post-war "economic miracle".But it's a myth. There was never full employment. The low unemployment of the post-war years is a massive statistical fudge. In fact, over five million people lost their jobs immediately after the end of the war, most of whom never worked again. But they were never listed as unemployed - because they were women. The Great Unemployment Fudge started in the "Depression of 1946", described by the Cato Institute as "one of the most widely predicted events
Topics:
Frances Coppola considers the following as important: Employment, GDP, recession, Unemployment, women
This could be interesting, too:
Ken Houghton writes Just Learn to Code
Angry Bear writes GDP Grows 2.3 Percent
Matias Vernengo writes Elon Musk (& Vivek Ramaswamy) on hardship, because he knows so much about it
Lars Pålsson Syll writes NAIRU — a harmful fairy tale
In the U.S., we are told, the post-World War II period was a golden age of full employment. High wartime government spending had brought to an end the double-digit unemployment and misery of the Depression, and as war gave way to peace, unemployment settled at a non-inflationary level of 3-5%. It's known as the post-war "economic miracle".
But it's a myth. There was never full employment. The low unemployment of the post-war years is a massive statistical fudge. In fact, over five million people lost their jobs immediately after the end of the war, most of whom never worked again. But they were never listed as unemployed - because they were women.
The Great Unemployment Fudge started in the "Depression of 1946", described by the Cato Institute as "one of the most widely predicted events that never happened in American history". During the war, there was full employment, GDP was roaring and industrial production was at an all-time high. But much of this was devoted to the war effort. Alvin Hansen was one of many economists warning that sudden cessation of wartime production and employment would plunge the economy back into Depression: “The government cannot just disband the Army, close down munitions factories, stop building ships, and remove all economic controls,” he said. Unemployment forecasts for demobilization ranged from 8 million to 20 million.
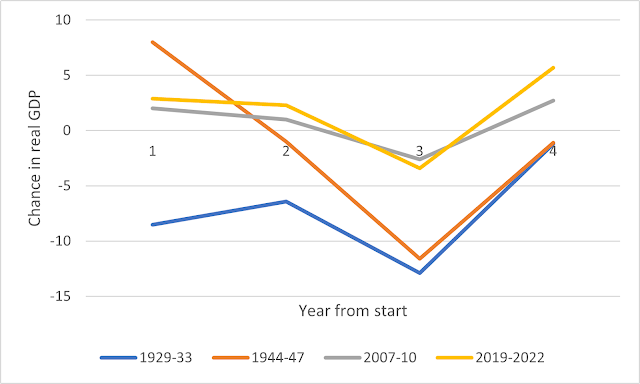
Understandably, policymakers were very worried. And with reason. Hansen's warning proved prophetic: as the war came to an end, the economy fell into a deep recession. The fall in real GDP in 1945-46 dwarfs both the Great Recession and the Covid-19 recession. Only the Great Depression was worse:
(source: BLS)
BLS figures show that the fall in real GDP was mainly caused by deep cuts to government spending: in 1946, government spending fell by nearly 65%, and by 1948 the government was running a budget surplus. But private sector consumption and investment increased. There was quite a boom in residential construction. As has happened so often in U.S. history, the housing market pulled the economy out of recession.
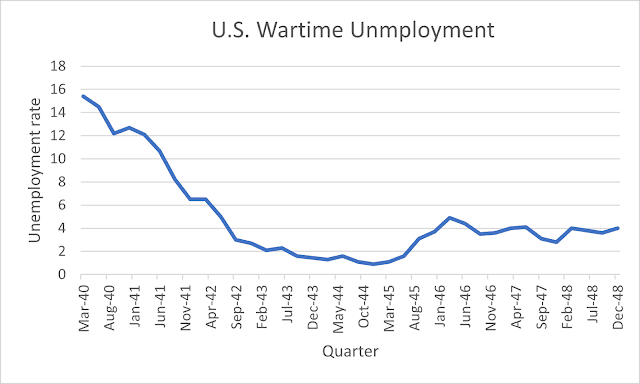
For the Cato Institute, the remarkable rebound in GDP and surprisingly low unemployment proved that worries about government spending cuts re-starting the Depression were unfounded. Blithely assuming away the counterfactual, they claimed that cutting government spending had kickstarted private sector investment and created 4 million new jobs. Unemployment was higher than it had been during the war, of course, but that's because mobilization had artificially depressed unemployment. After demobilization, unemployment rebounded to an average of around 4%:
It averaged about 4% for the next twenty years.
But it is extremely odd for unemployment to be so low in a recession of such severity. The Great Recession was in real GDP terms much less severe than the 1945-6 recession, yet unemployment rose to 10%. I wondered if something was artificially depressing the reported unemployment figures for 1945-6. So I went on a hunt.
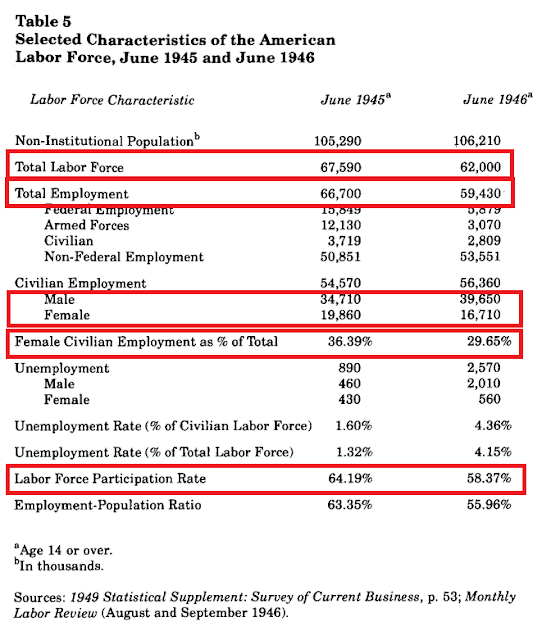
I didn't have far to look. This table from a a research paper by the Cato Institute economists Vedder & Galloway - the same people who claimed that the "Depression of 1946" never happened - shows that the increase in joblessness immediately after the war was far higher than the reported unemployment figures. I've highlighted the relevant figures.
As we might expect in a period of demobililization, armed forces employment fell sharply and civilian employment rose. Federal employment also fell as a result of the government's budget cuts, and non-federal employment rose. This rebalancing from military and government employment to private sector civilian employment shouldn't have caused a fall in the labour force. Yet it did. The first highlighted line shows that between 1945 and 1946, the total labour force shrank by nearly 6 million people.- Employers, particularly in manufacturing, were encouraged to replace women with returning veterans, and enthusiastically did so:
1946 USES report on the airframe industry, for example, notes that employment opportunities were limited “almost entirely to veterans, who receive preference in nearly all plants” (War Manpower Commission 1943–1945, February 1946, p. 13). In 48 large plants with 160,000 total employees, 4,000 veterans were hired in December 1945, despite net employment declines of 2,000 jobs. A similar report on the rubber tires and tubes industry, which had been roughly 20 percent female since it became critical in mid-1944, noted “women to be displaced...many employers have indicated to the USES that they expect to replace most of the women on the production line with men” (War Manpower Commission 1943–1945, January 1946, p. 15).
- The federal government sharply cut the proportion of women it employed, from 38% during the war to 28% by the end of 1946. Simultaneously, it cut total federal employment by half a million jobs due to budget cuts. This reduction disproportionately fell on women.
- Although hundreds of thousands of women applied to the U.S. Employment Service (USES), they were largely ignored by the USES, which prioritised finding employment for veterans. Female placements dropped precipitously as men returned from the war:
Furthermore, to prevent women competing with veterans for placements, USES limited placements for women to the kinds of jobs they had done before the war, even though this meant women were less likely to get employment:The USES explained the drops in female placements at the time by noting that “women job seekers have become more sharply limited to the types of jobs which they had held before the war”
- Some women - notably in cities - were claiming unemployment compensation, which meant they were actively seeking work. Rose says employers actively discriminated against them:
Few employers were looking for them, however: 60 to 81 percent of jobs posted in USES offices in these cities specified “men only,” leaving two and half times as many female UC claimants as jobs open for women.
Rose also says that although the jobs available to unemployed men and women typically paid far below their previous earnings, the wage cuts were deeper for women - 49-53%, as opposed to 34-49% for men. - Women were "bumped" down into lower-skilled jobs to make way for men in higher-skilled jobs. This happened even in industries which traditionally had large female workforces:
The USES noted that in the hosiery industry, where two-thirds of employees were female, some women hired to knitting and machine-fixing jobs were “bumped” as veterans returned.
"Bumping" happened in the jobs market too. Rose observes that for unemployed women who had done semi-skilled clerical work during the war, the chances of finding a similar job after the war were extremely poor.
But I have much less sympathy for the blatant misrepresentation of unemployment figures and the poisonous claim that women "voluntarily" left the workforce. Had women still been counted as "available for work" in 1945-6, reported unemployment would have been in double digits - not as high as in the Great Depression at its worst, but certainly of the order of 10-12%, similar to the rates immediately prior to the war. And it would have stayed elevated for a long time. But that would have destroyed the myth of full employment, along with the notion that cutting government spending by 65% in one year can ever kickstart recovery and job creation.
So the Depression of 1946 very much did happen. And its effects were very long-lasting. It wasn't just women who worked during the war who were excluded from the post-war workforce. Women who were children during the war were too, and so were the early "baby boomer" women. Women didn't start to return to the workforce in significant numbers until the second half of the 1960s, and they were still being systematically discriminated against well into the 1970s.