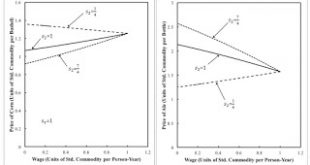
Figure 1: Variation of Prices of Production with Wages and Markups1.0 Introduction This post documents an example in my working paper, The Labor Theory of Value and Sraffa's Standard Commodity with Markup Pricing. 2.0 Technology Consider a simple economy in which corn and ale are each produced from inputs of labor, corn, and ale. Inputs for unit outputs are shown in the columns in Table 1. Obviously, the units of measure should not be taken serious. Inputs are totally used up in the...
Read More »Structural Economic Dynamics and Fake Switch Points
Figure 1: A Pattern Diagram with Joint Production1.0 Introduction This post completes an example. I analyzed bits of this example here and here. This post may make no sense if you have not read a long series of previous posts or, maybe, the papers highlighted here and here. I am interested in how and if my approach to analyzing and visualizing variations in the choice of technique with technical progress extends to joint production. The example suggests fake switch points do not pose an...
Read More »Variation in Standard Commodity with Relative Markups
I am not sure about the economic logic in this post. Maybe somebody like D'Agata or Zambelli could do something with this. These ideas were suggested to me by email with a sometime commentator. I start out with notation for Sraffa's price system, modified in an unusual way to allow for persistent variations in the rate of profits among industries: a0 is a row vector of labor coefficients in each of n industries. A is a Leontief input-output matrix, where ai, j is the quantity of the ith...
Read More »A Fluke Case Over The Wage Axis
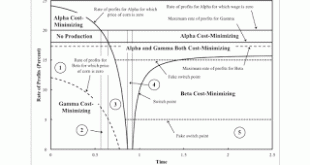
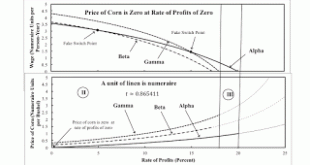
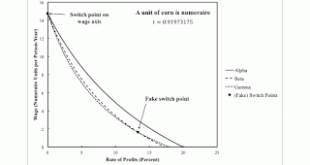
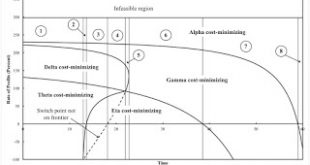
Figure 1: Wage Curves and The Price of Corn for the Fluke CaseIntroduction This post extends a previous post. I am basically introducing structural dynamics into an example, by Bidard and Klimovsky of fake switch points. At a rate of profits of zero in the example, the price of corn is zero for Alpha, one of the two techniques that is cost-minimizing there and for somewhat higher rates of profits. At a time before the fluke case, only the Gamma technique is cost-minimizing at a rate of...
Read More »A Pattern Over The Wage Axis In A Case Of Joint Production
Figure 1: Wage Curves with Corn as Numeraire1.0 Introduction This post presents an example of a fluke switch point in which the choice of technique cannot be analyzed by the construction of the wage frontier. Under joint production, the technique that is cost-minimizing, for a given rate of profits, does not necessarily maximize the wage. Nevertheless, one can still see what I call a pattern over the wage axis in this case. The example is a generalization of the numerical example in...
Read More »Structural Economic Dynamics And Reswitching In A One-Good Model
This post, as suggested, extends this one-good example. I assume a constant returns-to-scale technology, as specified in Tables 1 and 2. Labor is advanced to the capitalists, and wages are paid out of the surplus at the end of the year (period of production). The capitalists (incorrectly) expect the technology in existence at the start of the year to continue to exist. I assume prices of (re)production prevail. Table 1: Inputs for The Technology InputProcess(I)(II)(III)Labor30 eσ0,1(1 -...
Read More »Harrod-Neutral Technical Progress and Fluke Switch Points
Figure 1: A Pattern Diagram I have put up a working paper with the post title. Abstract: This article considers Harrod-neutral technical progress in the context of an analysis of the choice of technique. In a model of the production of commodities by means of commodities, neutral technical change is compatible with the reswitching of techniques, capital reversing, process recurrence, and the reverse substitution of labor. A taxonomy of fluke switch points is applied to an example,...
Read More »On Hicks’ Average Period of Production
Figure 1: APP Around Switch Points1.0 Introduction I take it that the Austrian theory of the business cycle builds on Austrian capital theory. The following two claims are central to Austrian capital theory: Given technology, profit maximizing firms adopt a more capital-intensive, more roundabout technique at a lower interest rate. The adoption of a more roundabout technique increases output per worker. Originally, Eugen von Böhm-Bawerk proposed a physical measure of the average period...
Read More »All Combinations of Real Wicksell Effects, Substitution of Labor
Figure 1: A Pattern Diagram Consider an example of the production of commodities, in which many commodities are produced within capitalist firms. Suppose two techniques are available to produce a given net output. These techniques use the same set of capital goods, albeit in different proportions. They differ in process in use for only one industry. Given the qualification about the same capital goods, generic (non-fluke) switch points are the intersection of the intersection of the wage...
Read More »Positive Real Wicksell Effect, Forward Substitution Of Labor
Figure 1: Wage-Rate of Profits Curves Consider a comparison of comparison of stationary states. Net output is taken as given, and a unit of net output is the numeraire. Technology consists of a finite set of techniques. In each technique, net output is produced from inputs of labor and produced circulating capital goods. No fixed capital is used, and land of the best quality is in such abundance that it is free. Also assume constant returns to scale. One can find a wage-rate of profits...
Read More » Heterodox
Heterodox